Aadhar Enabled Payment Service
What is AePS Service?: In today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, technology has played a pivotal role in shaping inclusive and accessible banking solutions. One such innovative service that has revolutionized the banking sector in India is the Aadhar Enabled Payment Service (AePS). This service has emerged as a game-changer, fostering financial inclusion and offering secure, convenient, and accessible banking services to every individual, especially in remote areas where traditional banking infrastructure might be lacking.
What is AePS Service?
Aadhar Enabled Payment Service (AePS) is an initiative by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) that allows bank account holders to carry out basic banking transactions using their Aadhar authentication. Aadhar, a unique identification number issued by the Indian government, plays a pivotal role in enabling transactions through AePS.
Understanding Aadhar Authentication in AePS:
Aadhar Authentication is the process wherein individuals provide their Aadhar number and undergo biometric or OTP-based authentication to access various banking services. This verification process ensures the security and validity of transactions performed through AePS. Till today, only Biometric Authentication is supported to complete the AePS Transaction.
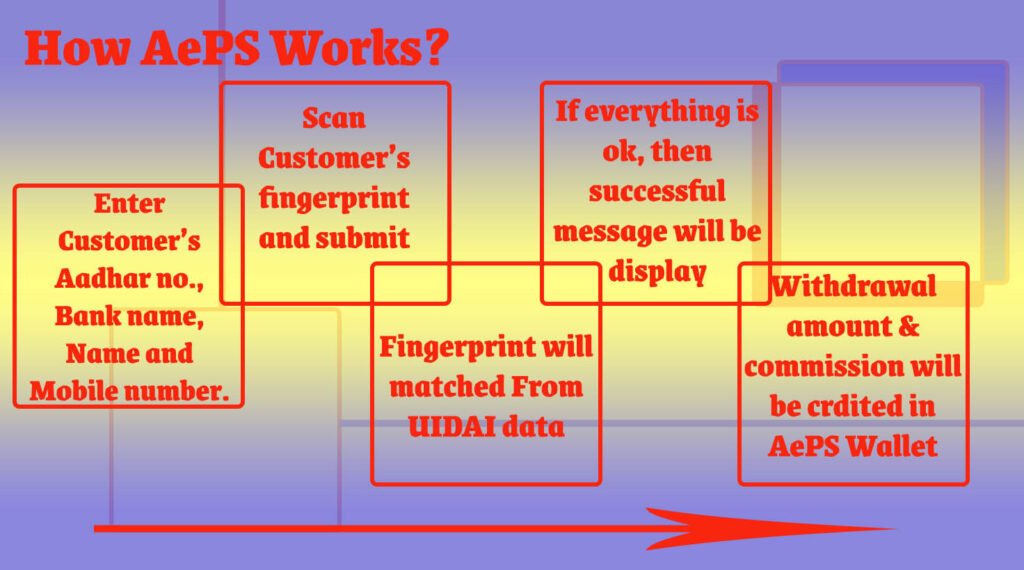
How AePS Works:
AePS leverages the Aadhar Card and biometric authentication to facilitate various banking services such as cash withdrawal, balance inquiry, mini statements, and more. Here’s a breakdown of how some of these services work:
Cash Withdrawal:
Individuals can withdraw cash from their bank accounts through AePS using biometric authentication at AePS-enabled micro-ATMs. These micro-ATMs, operated by retail agents or distributors, facilitate cash withdrawals.
Balance Inquiry:
Users can check their account balance through AePS by authenticating their identity with Aadhar and biometrics. This service provides instant access to account details without the need for traditional banking infrastructure.
Mini Statement:
AePS allows individuals to obtain a mini statement of their recent transactions by authenticating their identity via Aadhar and biometrics. This service aids in keeping track of transactions without visiting a bank branch.
Aadhar Pay:
AePS supports Aadhar Pay, allowing individuals to make payments directly from their bank account to the merchant’s account using Aadhar authentication, fostering cashless transactions.
Components Involved in AePS Transactions:
- Aadhar Card: The unique identification number issued by the government.
- IIN (Issuer Identification Number): This identifies the issuing bank.
- Acquirer Bank: The bank providing AePS services to customers through their agents or distributors.
- Issuer Bank: The bank where the customer holds the account.
OffUs & OnUs Transactions in AePS:
- OffUs Transactions: Transactions where the customer uses AePS services at a micro-ATM of a bank other than their account-holding bank.
- OnUs Transactions: Transactions where the customer uses AePS services at a micro-ATM of their account-holding bank.
Role of RD Service and Fingerprint Scanner in AePS:
Registered Device (RD) service ensures the security of biometric data captured during AePS transactions. The fingerprint scanner is an essential tool used for biometric authentication, ensuring accurate and secure identification.
Understanding AePS Error Codes:
AePS transactions may encounter error codes due to various reasons such as connectivity issues, incorrect Aadhar details, low balance, etc. These error codes help in diagnosing transaction failures for prompt resolution.
AePS Commission and Its Structure:
Banks, as well as retail agents and distributors, earn commissions for facilitating AePS transactions. The commission structure varies based on the type of transaction, volume, and involvement of different stakeholders. Also read about commission provided by different third party companies.
Driving Financial Inclusion through AePS:
AePS has been instrumental in driving financial inclusion by reaching the unbanked and underbanked populations in remote areas. It has empowered individuals by providing easy access to banking services, reducing dependency on physical bank branches.
Benefits of using AePS
Benefits of Aadhar Enabled Payment Service (AePS) for both customers and retail agents are given below:
| Benefits of AePS for Customers | Benefits of AePS for Retail Agents |
|---|---|
| 1. Accessible Banking Services: Enables customers in remote areas to access basic banking services conveniently. | 1. Increased Revenue Streams: Offers additional income opportunities for retail agents through commissions earned on AePS transactions. |
| 2. Financial Inclusion: Empowers unbanked and underbanked populations by providing them with banking facilities. | 2. Enhanced Footfall: Attracts more customers to retail outlets, increasing foot traffic and potential sales. |
| 3. Convenient Transactions: Allows customers to perform transactions like cash withdrawal, balance inquiry, etc., without visiting a bank branch. | 3. Strengthened Customer Relationships: Improves customer loyalty by providing them with essential banking services at retail agent locations. |
| 4. Secure Biometric Authentication: Offers secure authentication methods using Aadhar biometrics, ensuring transaction security. | 4. Technology Integration: Integrates technology into retail agent services, fostering a tech-savvy image and attracting more customers. |
| 5. Reduced Dependency on Cash: Facilitates Aadhar Pay, promoting cashless transactions, and reducing dependency on physical currency. | 5. Contribution to Financial Inclusion: Retail agents become instrumental in extending banking services to underserved populations, aiding in national development goals. |
Related Articles
- Aadhar Banking
- Aadhar Authentication
- OffUs & OnUS Transaction
- Mini Statement
- Cash Withdrawal
- Balance Inquiry
- Aadhar Pay
- RD Service
- Fingerprint Scanner
- AEPS Error Codes
- Server Issues
- IIN
- Acquirer Bank and Issuer Bank
- AePS Commission
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
What is Aadhar Enabled Payment Service (AePS)?
AePS is a service introduced by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) that enables basic banking transactions using Aadhar authentication. It allows individuals to access banking services through Aadhar biometric verification.
How does Aadhar Authentication work in AePS?
Aadhar Authentication in AePS involves individuals providing their Aadhar number and undergoing biometric or OTP-based verification. This process ensures the security and validity of transactions performed through AePS.
What are the basic transactions facilitated by AePS?
AePS facilitates various transactions including cash withdrawal, balance inquiry, mini statements, and Aadhar Pay, allowing individuals to perform banking activities without visiting traditional bank branches.
What role does Aadhar Pay play in AePS?
Aadhar Pay in AePS enables individuals to make direct payments from their bank account to a merchant’s account using Aadhar authentication, promoting cashless transactions.
What are OffUs and OnUs transactions in AePS?
OffUs transactions refer to transactions where individuals use AePS services at a micro-ATM of a bank different from their account-holding bank. OnUs transactions occur when they use AePS services at their account-holding bank’s micro-ATM.
How does RD Service and Fingerprint Scanner contribute to AePS security?
RD Service ensures the security of biometric data captured during AePS transactions. The fingerprint scanner, used for biometric authentication, plays a crucial role in accurate and secure identification.
Can you explain the components involved in AePS transactions?
Components include Aadhar Card, IIN (Issuer Identification Number), Acquirer Bank, and Issuer Bank. These entities together enable seamless AePS transactions.
What are Mini Statements in AePS, and how can they be accessed?
Mini Statements in AePS provide a summary of recent transactions. Users can access these statements by authenticating their identity through Aadhar and biometrics.
What are AePS Error Codes, and how are they resolved?
AePS Error Codes indicate transaction failures due to various reasons such as connectivity issues, incorrect Aadhar details, low balance, etc. These codes aid in diagnosing and resolving transaction issues promptly.
How does AePS contribute to financial inclusion in India?
AePS has significantly contributed to financial inclusion by providing accessible banking services to the unbanked and underbanked populations, especially in remote areas, reducing dependence on physical bank branches.
What is the commission structure for AePS transactions?
The commission structure for AePS transactions varies based on transaction types, volumes, and the involvement of different stakeholders such as banks, retail agents, and distributors.
How has AePS transformed the traditional banking system in India?
AePS has transformed the traditional banking system by introducing convenient, secure, and accessible banking services, reducing barriers for individuals in accessing basic financial services across the country.
Is AePS service free to use?
Yes, also no, some third party AePS service provider companies provide Retailer ID at no cost mean Free Retailer ID.
Conclusion:
Aadhar Enabled Payment Service (AePS) stands as a testament to India’s commitment to inclusive and accessible banking services. By leveraging Aadhar authentication and innovative technology, AePS has revolutionized the banking sector, making basic financial services accessible to all. With its array of services, secure authentication methods, and outreach to remote areas, AePS continues to bridge the gap in financial inclusion, transforming the way individuals access banking services in India.



